HCDD 340
Layout
Recap from last class
- Dimension: Percentage
Dimensions: percentage
Relative to some other dimensions
div {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
}
div p {
width: 50%;
}<p>: 50% width of the parent div
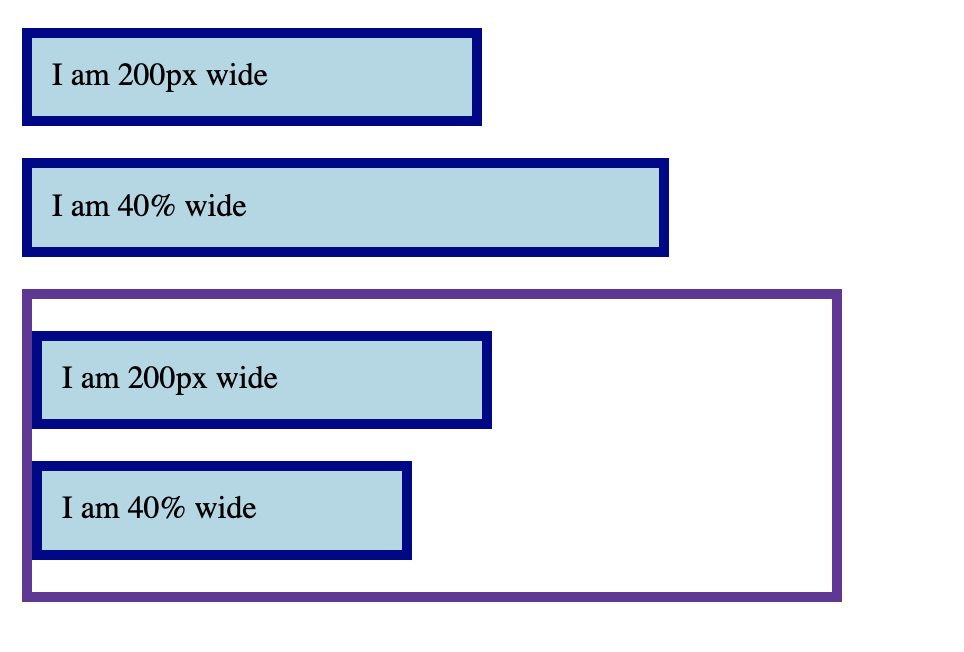
Dimensions: percentage
.box {
background-color: lightblue;
border: 5px solid darkblue;
margin: 1em 0;
}
.wrapper {
width: 400px;
border: 5px solid;
}
.px {
width: 200px;
}
.percent {
width: 40%;
}<div class="box px">
I am 200px wide
</div>
<div class="box percent">
I am 40% wide
</div>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="box px">
I am 200px wide
</div>
<div class="box percent">
I am 40% wide
</div>
</div>Percentage width is calculated from the parent
Today
- Box model
- Layout flow
- Float
- Positioning
- Flexbox
Everything displayed in CSS is a box!
The Box Model
- Each element has a rectangular box
- text
- elements that looks circular
Check the circular images in the lab page
- Inspect -> Layout (Firefox)
- Inspect -> Computed (Chrome)
How does the box model work?
It is all box stacking
Putting boxes together to show the page
Outer display type
- How boxes are laid out in relation to other boxes
Inner display type
- How elements within the box are laid out
Block boxes
<h1>, <p>, …
- The box will break into a new line
- If width is not specified
- will use up available space within parent
Inline boxes
<span>, <a>,
…
- The box will not break into a new line
widthandheightcan’t be set- If there is no space, then the overflow will continue to a new line
Inline Block boxes
- The box will not break into a new line
- But, you can set
widthandheight
You can change box display types
Set the display
property
.inline {
display: inline;
}
.block {
display: block;
}<p class="inline">First inline para.</p>
<p class="inline">Second inline para.</p>
<p>Another <span class="block">para with span.<p>Box model areas
Box model areas
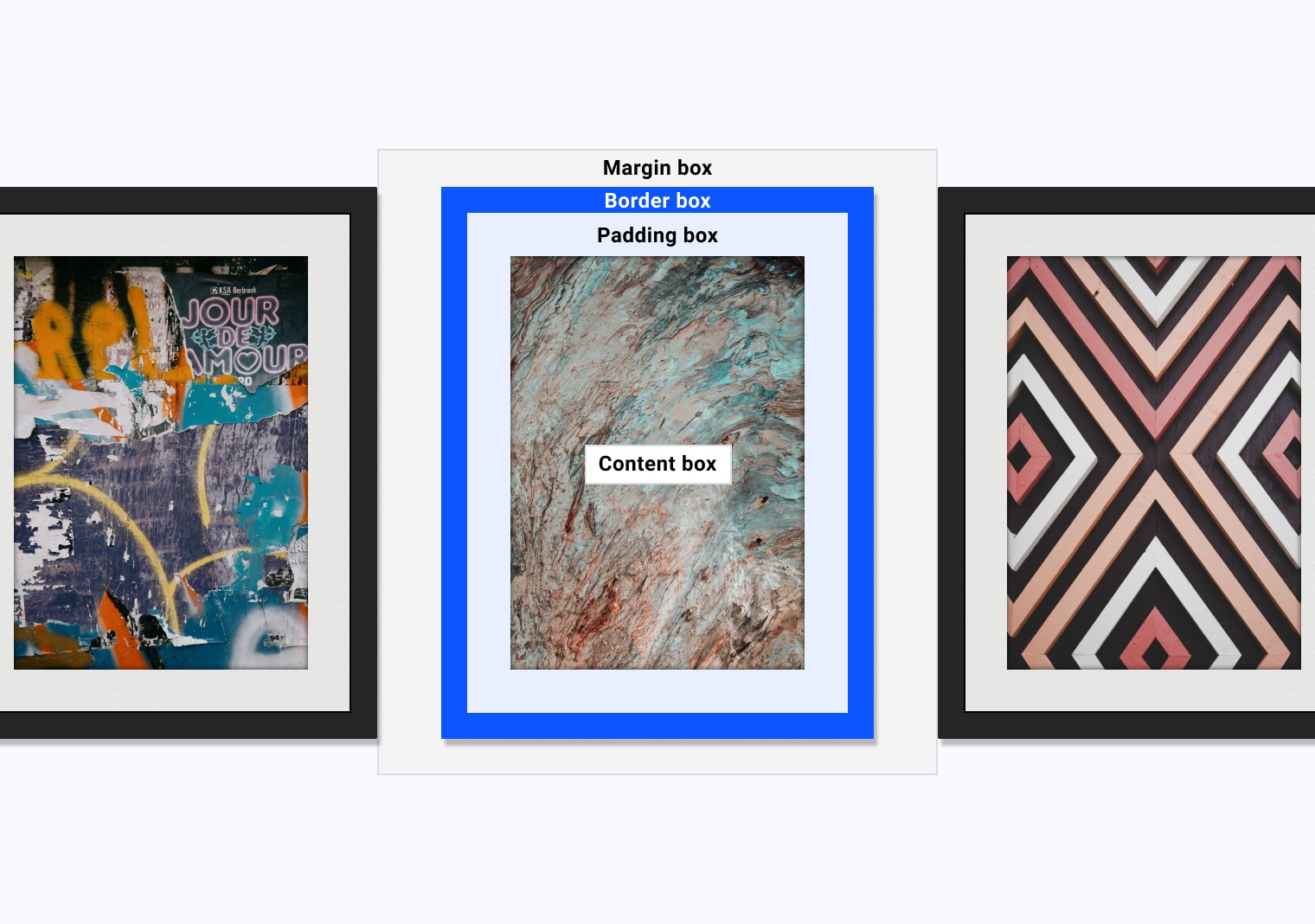
Box model areas
- Content
- Padding
- Border
- Margin
Controlling the box areas
heightandwidth- applies to
contentbox
- applies to
paddingandborder- adds to
contentbox sizes
- adds to
margindoes not count to box size- it is the outside space
What’s the total height and width here?
.box {
width: 350px;
height: 150px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 25px;
border: 5px solid black;
}What’s the total height and width here?
.box {
width: 350px;
height: 150px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 25px;
border: 5px solid black;
}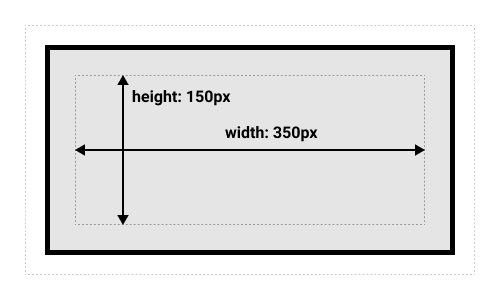
- Width: 410px
- 350 + 25 * 2 + 5 * 2
- Height: 210px
- 150 + 25 * 2 + 5 * 2
This default rule is 👎🏾
Inconvenient to add padding and border to get actual box size
Alternative box model
box-sizing: border-box;
- Height and width applies to the box
- instead of the content
- Border and padding get pushed in
- content = box - (border + height)
- More predictable
What’s the total height and width here?
.box {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 350px;
height: 150px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 25px;
border: 5px solid black;
}What’s the total height and width here?
.box {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 350px;
height: 150px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 25px;
border: 5px solid black;
}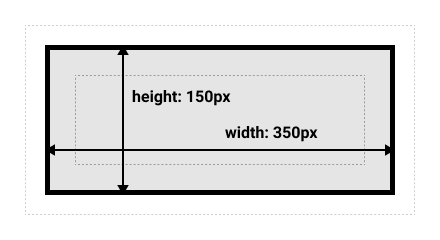
- Width = 350px
- Height = 150px
Box models


This default rule is 👎🏾
Inconvenient to add padding and border to get actual box size
- Todo
- Go to the activity from our last class
- Make the inner box width same as the
wrapper
Todo
Now use the alternative box model:
html {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
*,
*::before,
*::after {
box-sizing: inherit;
}More predictable height and width
Alternative box model is more common
html {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
*,
*::before,
*::after {
box-sizing: inherit;
}Today
- Box model
- Layout flow
- Float
- Positioning
- Flexbox
Float
- Takes an element out of the normal box stacking flow
- Places it left or right side of the parent
- Other inline elements will “float” (“wrap”) around it
- Mostly for image and text
Float
.box {
float: left;
}<div class="box">Float</div>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
</p>Can you float it to right?
Today
- Box model
- Layout flow
- Float
- Positioning
- Flexbox
Positioning
- Mostly for elements out of the normal flow. E.g.,
- Adding a caption on top of an image
- Fixed tab header
- Image that overlays over other elements
- Options
- static (default), absolute, fixed, sticky
Relative Position
- Element placed following the normal flow
- You can move the final position
top,bottom,left,rightvalues
Check it out!
Absolute Position
- Element moves out of the normal flow
- Sits on a separate flow
- great for isolated UI features
- tab controls, menus, …
- great for isolated UI features
top,bottom,left,rightvalues- placement within the
containerelement
- placement within the
Absolute Position
What’s the container element
- Any ancestor element with their
positionexplicitly defined- Default is the
<html>element
- Default is the
Todo
- Open Activity 03
- In
.absoluteclass:- Set
position: absolute
- Set
- Change
topproperty- To place the element before “Overview”

Todo
- Now in
index.html, set:<div class="relative">
- Where does the
<p>move?- Why?
Absolute Position
What’s the container element
- Any ancestor element with their
positionexplicitly defined- Default is the
<html>element
- Default is the
Fixed Position
Fixed in relation to the viewport
- Persistent element always visible
See the example
Today
- Box model
- Layout flow
- Float
- Positioning
- Flexbox
Flexible Box Layout model
Modern approach to layout
section {
display: flex;
}Flexbox
- Single dimension layout
- Arrange items in rows or columns
Flex model
- Main axis
- Direction of how items are laid out
- row or column
- Cross axis
- The other direction
- Parent element
- with
display: flex
- with
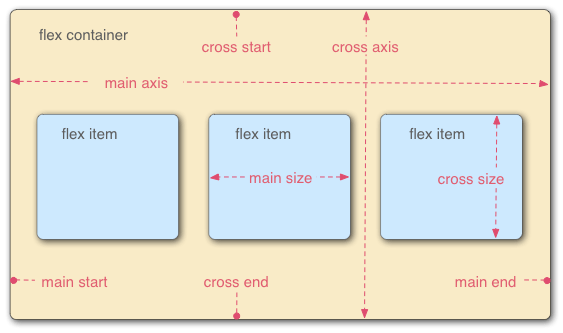
Main axis direction
Default is row
/* Set main axis to column */
flex-direction: column;Wrapping
Items overflow by default

Not good for most cases
Wrapping to next line
flex-wrap: wrap;


flex-wrap: wrap;flex-flow shorthand
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;=
flex-flow: row wrap;Todo
- Open Activity 04 in Firefox/Chrome
- Go to Dev Tools –> Layout
- Firefox: “Flex Container”
- Chrome: “Flexbox”
- Select
section
- Select
- Set flex direction to be
column
Change it back to row
Todo
- Change Browser width
- Check the page in “iPhone”
- What happens?
Enable wrapping
Flexible sizing of items
A key advantage!
- Allows responsive design
Flexible sizing of items
flex: proportion
values
- How much available space an item will take
- compared to other flex items
- along the main axis
What’s the size of each item?
3 items — each with flex: 2;
Each will have same size
What’s the size of each item?
3 items
/* first item */
flex: 1;
/* second item */
flex: 1;
/* third item */
flex: 2;Item 3 twice the size of Item 1 and 2
Flexible sizing of items
Allows setting minimum sizes
/* at least 100 px */
flex: 1 100px;flex: auto
- Absorbs available space
- Shrinks to minimum size when necessary
Todo
- Open Activity-04 again
- Make Penn take 1/3 of
all space
- Each item should be at least 150px wide
Today
- Box model
- Layout flow
- Float
- Positioning
- Flexbox
